Careful people may find that in the last decade of development, the interface of display devices has undergone tremendous changes! We used a lot of blue VGA interface, and then there is a white DVI interface. When encountering different interfaces, we have to buy adapters for transfer. Later, there was an interface such as HDMI, and now there are DP and USB Type-C interfaces. So, with so many interfaces, what is the difference? Which one should we use?

VGA Port
The VGA interface is also known as the D-Sub interface. In the era of CRT displays, the VGA interface is a must. Because CRTs are analog devices, and VGAs are analog protocols, they are of course matched for use. The VGA interface adopts a 15-pin pin structure, which transmits signals such as components and synchronization. It is the interface used by many old graphics cards, notebooks and projectors. Later, the LCD display appeared, also with a VGA interface. The display has an A/D converter built in to convert the analog signal to a digital signal for display on the LCD.
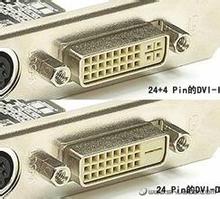
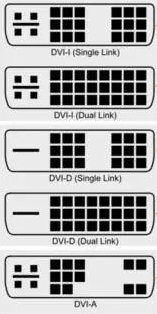
DVI Port
There are many types of DVI, DVI-A, DVI-D, DVI-I on the interface, and can be divided into single channel and dual channel. The DVI-A (DVI-Analog) interface only transmits analog signals. The essence is the VGA analog transmission interface specification, which is often used to transfer the DVI-I output of the graphics card to the VGA display interface. The DVI-D (DVI-Digital) interface is a pure digital interface and is not compatible with analog signals. DVI-I (DVI-Integrated) interface, compatible with DVI-I and DVI-D plugs, compatible with digital and analog signals. Their interface shapes are different and cannot be inserted if the interfaces do not match.
HDMI Port
The HDMI interface was introduced in 2002 and has now evolved to the HDMI 2.1 standard. With the development of the industry, the HDMI 2.1 standard has been able to support 4K 120Hz and 8K 60Hz, and supports high dynamic range imaging (HDR), which can be optimized for scenes or frames. Backwards compatible with HDMI 2.0 and HDMI 1.4. The main thing is that it is transmitted simultaneously with video and audio.
Many of today’s monitors have built-in speakers, and with an HDMI cable, you can simultaneously transfer images and sounds, which is a big advantage of HDMI. Because of this, HDMI is the most common interface for today’s displays. We should also prefer this interface when we use it. There are several types of HDMI on the physical interface. There are mainly standard HDMI interface, mini HDMI interface and Micro HDMI interface. For long-distance transmission of HDMI cable, the wire is generally hard, so try to use a device with a standard HDMI interface to get a stable connection. The Mini HDMI interface and Micro HDMI interface are more suitable for small devices.

DP Port
The DP (Display Port) interface is a competitor of the HDMI interface. On some graphics cards and displays, in addition to the HDMI interface, it also has a DP interface. At present, the DP interface has been developed to version 1.4, which can transmit 10bit 4K 120Hz video, and can also support 8K 60Hz video. DP1.4 is compatible with the USB Type-C interface, which means that we can use the DP1.4 protocol to simultaneously transmit HD video while USB 3.1 is transmitting data. From a trend perspective, this is very beneficial for promoting the upgrade of peripheral audio and video equipment. Moreover, the DP interface can also transmit sound synchronously on a single line to achieve the use of the display sound.

Type-C Port
The USB interface has long been known. In the past, the USB interface was designed to transmit data, so it is very common in the use of storage devices such as mobile hard disks. Now USB 3.1 Gen2 has reached 10Gbps speed, and the design standard can also meet the video and data transmission, so on some monitors, the USB 3.1 interface can also be found. The current USB 3.1 interface has been able to meet the resolution display of 4K 30P, which is roughly the same level as HDMI1.4. However, it will be upgraded in the future and will become the most common display transmission method. It should be noted that USB 3.1 Gen1 is USB 3.0, and USB 3.1 Gen2 is the real USB 3.1.
The advantage of the Type C interface is that it can be plugged and unplugged. Some Type C interfaces also have the functions of data, power and signal transmission. When applied to the display, it can bring a lot of convenience. Type C notebook users can charge and connect the display through an interface, and can also use the USB interface extended on the display, greatly reducing the burden on the notebook.

